Soil oxygen sensor
Soil Oxygen Sensor MIJ-03
Soil oxygen sensor MIJ-03 developed by our company Environmental Measurement Japan in April 2006. MIJ-03 soil oxygen sensor is used for the measurement of the root aspiration. MIJ-03 detects the density of oxygen in the soil by % order without any difficulties, it simply digs up the hole in the soil and lay this sensor into the ground. An usual usage of this sensor is laid in a vertical direction at intervals of 20 to 50 cm. Researchers can measure the vertical profile of the O2 in the soil.
Why we recommend our MIJ-03?
Soil Oxygen Sensor MIJ-03 is built from a rigid thermoplastic, that allows long-term stability in most environmental conditions; thus it’s life time is maximum about 10 years.
Most users are not willing to maintenance the sensors; MIJ-03 is friendly to those users because it need only minimum maintenance. Once the sensor is installed in the soil, you do not need to care about maintenance.
MIJ-03 can be connected to EMJ data logger MIJ-12 or MIJ-01. If you have your own data logger you may be able to connect MIJ-03; this is because it has a voltage output that can be supported by any compatible data logging system.
Features
・Can be used for long term observation with easy set-up
・Automatic temperature compensation
・No influence by the rain or other waters
・Easy span calibration
・Not require to do the zero calibration. 0% Oxygen = 0 mV output
Difference between dissolved oxygen sensor and soil oxygen sensor MIJ-03
Soil oxygen sensor MIJ-03
Since soil is rarely flooded, an soil oxygen sensor MIJ-03 developed to solve the problem that the dissolved oxygen sensor cannot measure for long term measurement because dissolved oxygen sensor need water to measure oxygen. Since MIJ-03 structure does not care for direct contact between the electrodes and the soil so no maintenance need and permanent installation is possible. The normal measurement range is 0 to 20.9%. Soil oxygen can never be higher than 20.9% of atmospheric oxygen. As a special case, rice field have a period of both flooding and drainage so both dissolved oxygen sensor and soil oxygen sensor MIJ-03 are often use together for this particular field.
Dissolved oxygen Sensor
Sensor that measures oxygen dissolved in water. The normal measurement range excluding supersaturation is 20mg/L measured in ppb units.
In the case of permanent installation, be careful of electrode contamination.
Setting Image
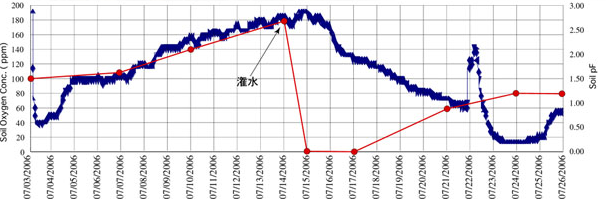
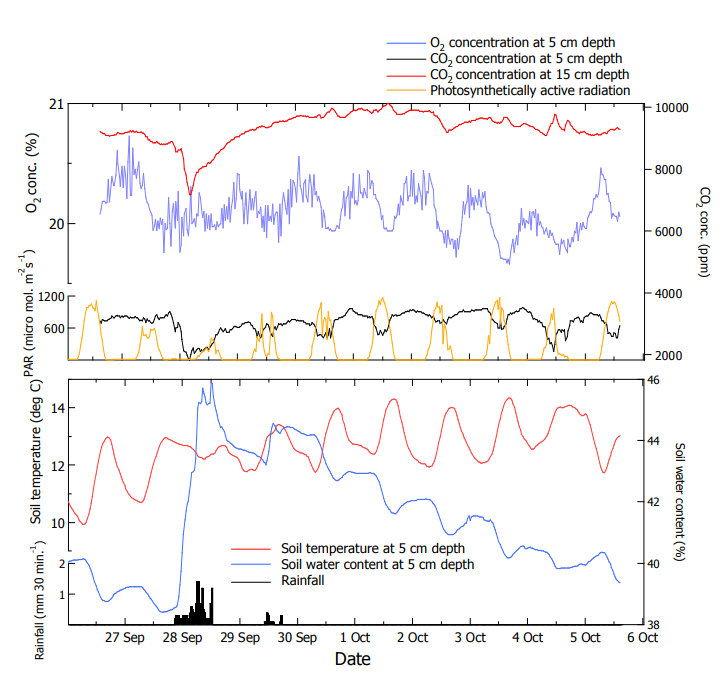
There are various ways to use it, such as burying the MIJ-03 in combination with a data logger at thedesired depth, measuring the depth direction profile, and measuring the horizontal distribution.

Figures
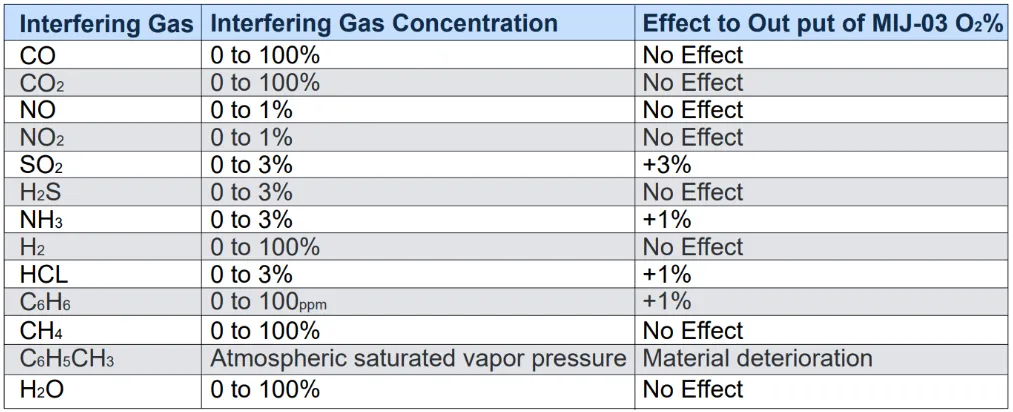
Interfering GAS
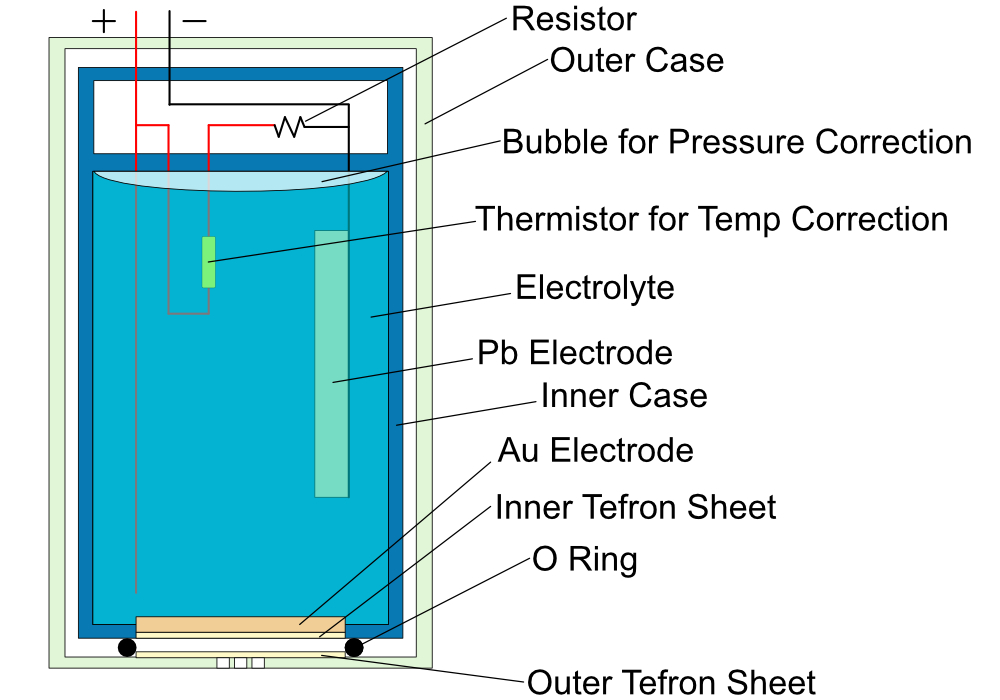
How it works & Schematic

Detects oxygen in soil simply by burying
(Data logger sold separately)
Specifications
| Theory | Galvanic Battery + Porous membrane sheet |
| Shape | 40mm, Length 78 mm (Cable support joint is 50mm height extra.) |
| Output | 45 – 65mV at 20.9%O2 (Users must check the output at the air before set-up) |
| Weight | 220g(Including cable) |
| Cable Length | 5m (+/White, -/Black, Shield cable) |
| Temperature Effect | At R.H. 100 % and O2 20.9%. Sensor out put is 20.8% at 5, 19.4% at 40degree. At R.H. 0% and O2 20.9%. It is not influence from the temperature effect |
| Temperature range | 0~40℃ (-10~60℃ with Temperature compensation) |
| Data collection | You need to prepare or purchase data logger (Sensor itself does not show the value) |
Temperature compensation
Temperature correction may be required to obtain accurate MIJ-03 values.
Temperature compensation is not required when the standard operating temperature is 0 to 40℃, but temperature compensation is required when the usage environment exceeds 40℃.
In this case, the sensor temperature must be recorded both when calibrating the MIJ-03 and when it is buried.
The following items are required to perform temperature compensation.
・Data logger (2ch or more)
・Temperature sensor (our NLTP is also recommended)
・MIJ-03
For details on the temperature correction formula, please download the file from the download button below.