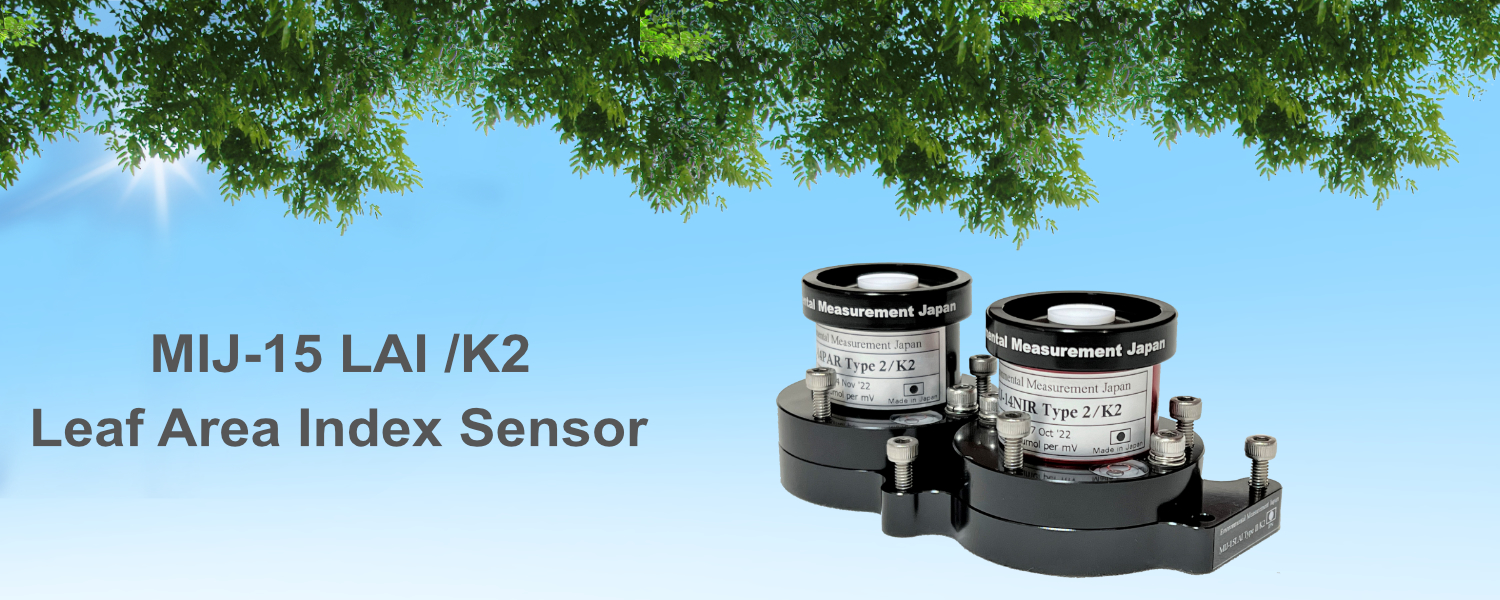


LAI sensor MIJ-15LAI TypeII/K2 : gives you Absolute LAI result
Overview
There are two methods for measuring the Leaf Area Index (LAI): direct estimation and indirect estimation. Direct estimation methods include reaping methods and litter traps method. Indirect estimation methods include a method using hemispherical photograph using a camera and a fisheye lens, and a method based on optical assumptions regarding the number of leaves and light attenuation.
In the recent trend, some companies selling instruments to measure LAI named as plant canopy analyzer. The measurement principle used in these instruments are that it detects the ratio of light intensity inside and outside the canopy. Thus, it is necessary to compare the data global solar radiation and the data under the canopy at the same time, based on the absolute value of inside and outside light. In addition, it depends on the azimuth angle of sunlight so that it requires manually performed at the same solar altitude in cloudy weather when the solar radiation intensity is relatively stable for these reasons.
Most significant fact is that these instruments are ignoring PAI such as branches and dead leaves; thus, they are not giving absolute LAI.
The relationship that the ratio of transmitted light correlates with LAI when PAR (400-700 nm) and NIR (700-1000 nm) are reflected and absorbed by chlorophyll in the leaves. MIJ-15 LAI sensor adopted the measurement method by spectroscopy (Patent No. JP5410323B22014.2.5). Therefore, it is possible to stably measure the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) absorption rate and LAI regardless of the weather. In addition, it is possible to obtain continuous data simply by installing this unit inside the canopy without installing the sensor outside the canopy. When this unit is installed with a data logger, the annual change of LAI can be measured in an unmanned stationary manner. Also, if you use the portable type, you can measure in a wide range while carrying around.
Features
・True LAI measurement that reacts only to sites containing chlorophyll
・Neglecting PAI (PAI: Measured values including dead leaves, branches, trunks, etc.)
・The world’s only sensor that adopts a relationship in which the intensity ratio of PAR and IR correlates with LAI.
・The accuracy is much more accurate than the fisheye lens type
・MIJ-15 LAI K2 : Unmanned, continuous, automatic LAI sensor (Required in combination with data logger)
LAI sensor MIJ-15LAI /K2
LAI is slowly changing parameter so that researchers may annoyed because when measuring manually, you have to do a huge amount of work both in terms of time and effort. But MIJ-15LAIK2 is only set under the canopy and you can wait till year end.
Many LAI instruments simultaneously measure the intensity of light under the canopy and the intensity of light outside of the canopy, measurement principle is that the obtained ratio correlates with LAI. Therefore, the effect of the growth of branches and trunks blocking the light directly affects the measured value. Also, in the autumnal tree species, the leaves without chlorophyll also block the light. In other words, it is unavoidable that dead leaves are counted as LAI.
On the other hand, in MIJ-15LAI, the measurement principle is that the ratio of the near-infrared light of chlorophyll contained in leaves and the spectral transmittance of PAR correlates with LAI so it do not count dead leaves, branches, trunks, electric wires and other artificial objects that have no chlorophyll.
MIJ15 LAI/K2 sensor provide with 5m cable so it must use with data logger. Sensor itself is same as PAR sensor MIJ14 which has a reputation for its extremely small long-term drift and robustness; this sensor intended to be permanently installed field and operated unattended.
This design has a proven track record of less than ± 0.1%/3 year drift unless destroyed in an accident. Much more durable than LAI sensors made by other companies.
Absolute quantity of LAI
MIJ-15LAI/P and MIJ-15LAI Type2/K2 will let researchers to determine absolute quantity of LAI by measuring the spectral ratio of sunlight transmitted through plant canopy.
How?
We used the measurement by spectroscopy.
(Patented NO.JP5410323B22014.2.5)
PAR(400-700nm) and NIR(700-1000nm) will be reflect and absorption occur at chlorophyll inside leaf so the transmitted light ratio is correlated with LAI.
MIJ-15LAI Type II /K2 gives numerous hopes for the feature research.
You do not need to think about weather condition and LAI and PAR can be measured just set under the canopy or leaf. Also, you only need to have one MIJ-15LAI Type II /K2 so price will be reasonable and it is portable so you can measure easily or traditionally set it at canopy; LAI annual change can be measured with data logger.
Options
Data Logger MIJ-01
Mounting Bracket
If you plan to set to the pole you may need mounting bracket.

Related Product
MIJ-15 LAI/P Portable type
If you prefer the portable LAI sensor then please see below MIJ-15LAI/P.

Specifications
| Measurements Range | 0〜5,000μE |
| Output |
Voltage (Calibration Coefficient labeled as ###.##μE/mV) System Sensitivity: ・NIR/5mV at 1300uE |
| LAI arithmetic expression | LAI=2.80In(NIR/PAR)+0.69* *Kume et al.(2011) J Plant Res124:99_106. |
| Temperature effect | <±0.1%/DEG |
| Unit |
PAR & NIR: uE(μmol・S-1・m-2) LAI: dimensionless |
| Response | 0.2u/Sec |
| Incidence angle characteristics | <±1.5% at 0〜79°(< -50%Peak at 80〜89°) |
| Angle of rotation characteristics | <±0.5% over 360° at 60°elevation |
| Material | Case:A5052, Coating: anodized aluminum, Diffuser: PTFE |
| Temperature Range | -40〜80℃ |
| Shape | 126mm(W), 60mm(D)×49mm(H) |
| Weight | 500g |
| pin assignment | White/output+, Black/output- |
| Standard Pack | MIJ-15LAI TypeII/K2 (With 5m cable) |